The American Heart Association Statement:
American Heart Association Physical Activity Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine; and Stroke Council.Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: a case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association
(2016) Click Here
V02 CPX Testing, the gold standard for assessing health and fitness. Read the AHA Statement: ( CLICK HERE)
It has been know since 1995 that poor CRF is an independent risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality (1). A recent publication in JAMA Network Open, established that poor CRF increases a persons risk of all-cause mortality to the same level as having type II diabetes or smoking (2). Smokers and type II diabetics have a 40% greater odds of all-cause mortality than their non-smoking and non-diabetic counterparts. These are significant increases in hazard ratios that are easily avoided.
Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)
World Health Organization (WHO) Report: An estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2019, representing 32% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, 85% were due to heart attack and stroke.
Most cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by addressing behavioural risk factors such as tobacco use, unhealthy diet and obesity, physical inactivity and harmful use of alcohol. (WHO)
World Health Organization 2019
The most fundamental cause of our modern diseases, such as Heart Disease, Prediabetes / Diabetes, Obesity, Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Cholesterol Disorders, Fertility and Reproductive Disorders, is a poor diet! Our diet and sedentary lifestyle are killing us. We can help! Dr. Paul
Now You Can Do Something About It!
- We lose our health slowly and quietly! After the age of 30, we can lose 1-2% per year, that is 10 – 20% per decade.
- Too many of us have entered into our fifties and sixties having lost 30-40% of our health.
- The greatest loss of health occurs between our 30s and 40s
- We are often unaware of how poor our health has become
- We are unaware of our increased risk level for serious health consequences. These include heart attack, stroke, cancers, diabetes, arteriosclerosis, obesity, COPD, etc.
- Unfortunately, many of us are unaware of our poor health status until we experience a serious health crisis.
What You Need to Know that You May Not Know!
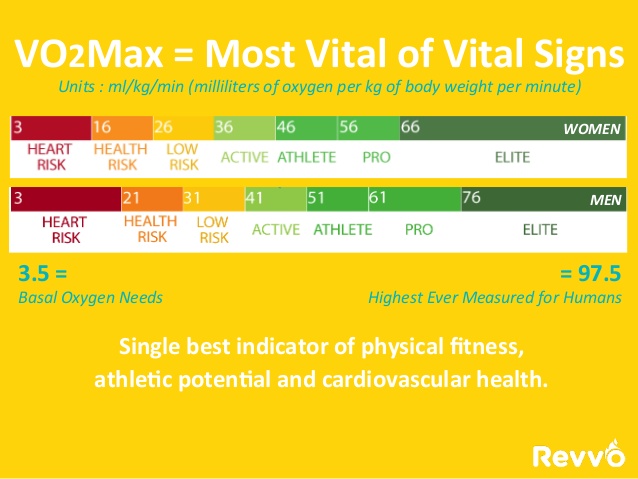
- The Best New Metric for measuring health status, risk assessment, and the future prognosis of your health is V02 CPX Testing
- Traditional Standard health and risk assessment metrics are:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia)
- T2DM (Type 2 Mellitus Diabetes)
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Traditional Standard health and risk assessment metrics are:
- V02 CPX is a stronger predictor then all these. Stronger assessment of health, and stronger predictor of future health.
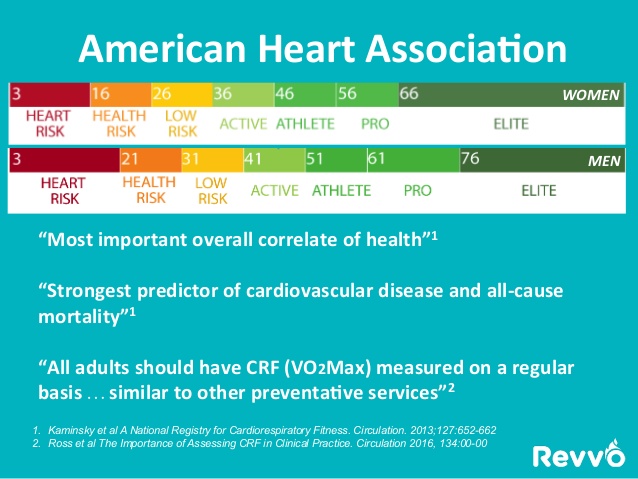
- Look at the right side top column at the “American Heart Association” blue box image. Click on it!
- In 2016 the American Heart Association stated the following about V02 CPX Testing:
- “Most Important Overall Correlate of Health”.
- “Strongest Predictor of Cardiovascular Disease and ALL-CAUSE Mortality”.
- “All adults should have CRF (Cardiorespiratory Health and Fitness) measured on a regular basis… similar to other preventative services”.
- American Heart Association Study – Click Here!
- V02 CPX Testing is the single most important step you can take for your health.
- Invest in Yourself ! If you do not take care of yourself, who will?
- Our office is on a Mission to Help People Invest in their Health and Invest in Themselves!
- Don’t Wait Until a Health Crisis Hits You! Do it Now!
Everyone capable of testing should test!
V02 Testing is the “Gold Standard” for testing cardiorespiratory health and fitness. In fact, it has been used by Olympic athletes for decades, and by Cardiologists performing CPET (Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing). V02 CPX Testing has and is being used Predominately in Medical Universities and Medical Research Organizations and Facilities. Unfortunately, V02 testing has been limited to a very small part of the population.
We are bringing V02 testing into the general population for medical evaluations, health screening, risk assessment, athletes and competitors, and especially for parameters and steps needed to regain or improve one’s health. Our True Health Program is designed to create a long term health improvement plan by one of our doctors and the individual.
If your an Athlete, then you know the value of V02 testing in order to measure and know your current V02 Max and Aet and AT Thresholds, and specifically your aerobic range. Then your training has more specificity and direction, helping to increase your power and endurance.
There is no age limit, we have tested 78 year olds. Even if you are in very poor health, we often have a way to test you.
If you are interested in improving your health, regaining your health, or at least stopping the loss of more health, then this is what you are looking for. Dr. Paul
Who Should Be Tested? - Everyone!
Why Should One Be Tested?
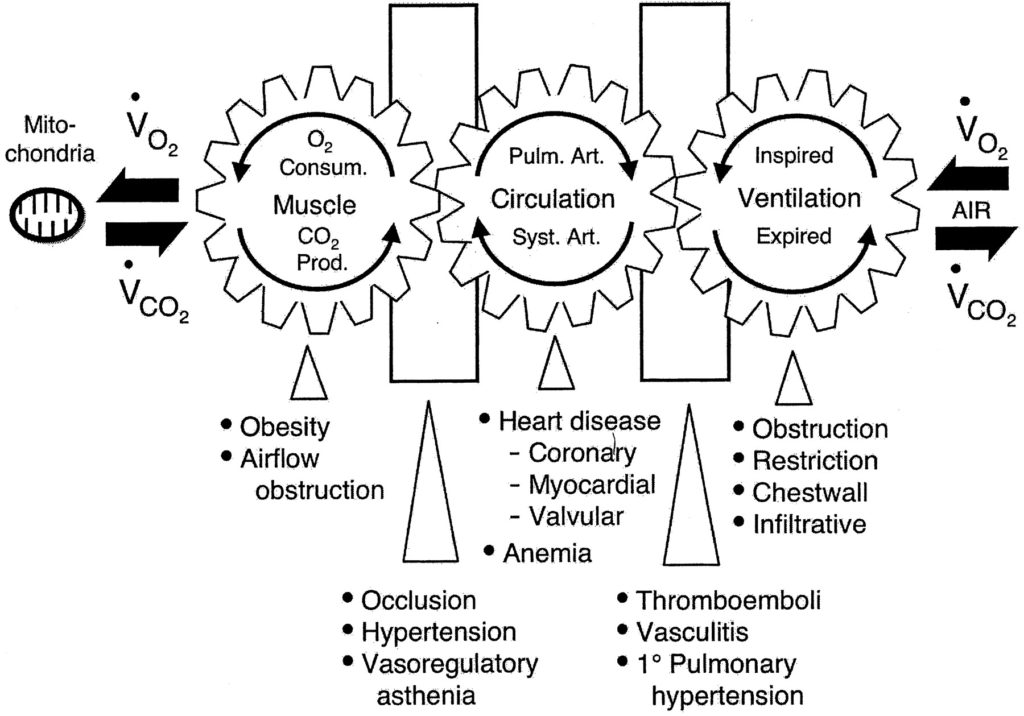
The foundation of human life and health is tied to Oxygen Metabolism. In other words, it is used to produce almost all of the energy (ATP) of the body. The energy to support life and its changing levels of physical activity is obtained from the oxidation of metabolic substrate.
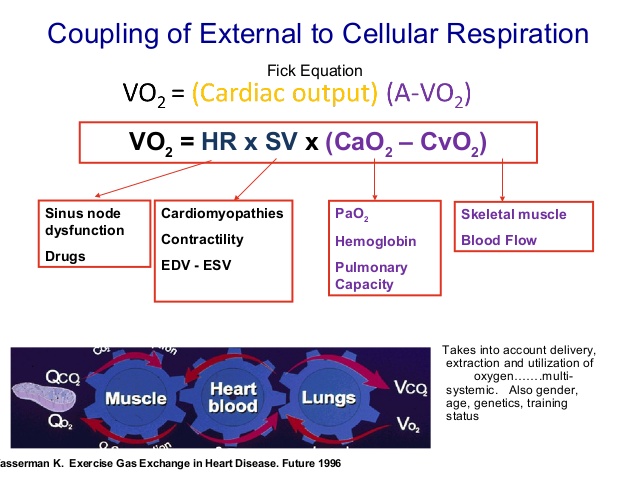
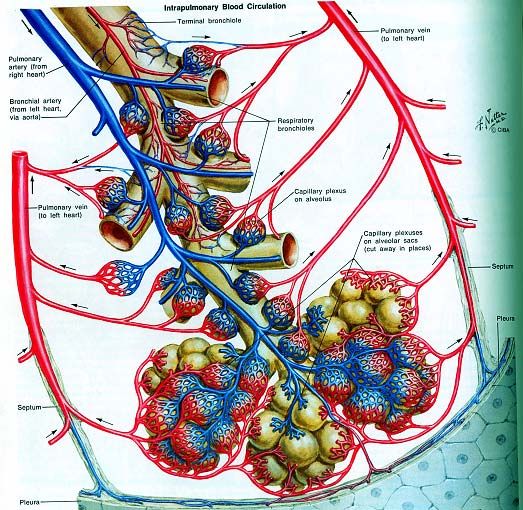
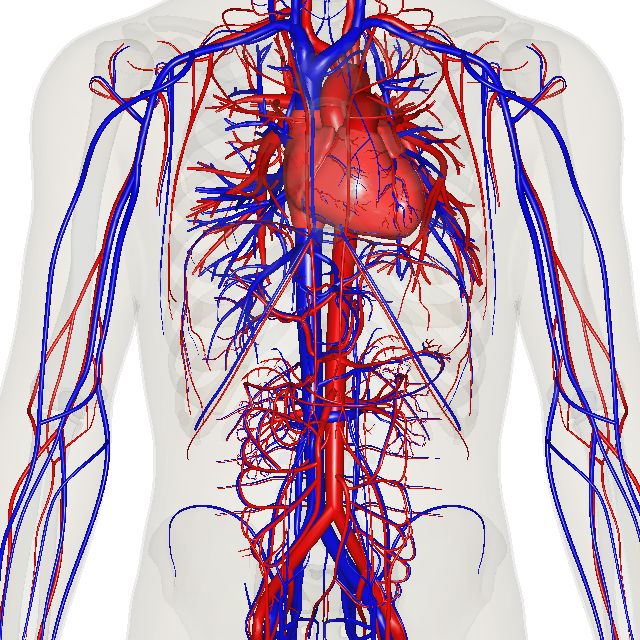
V02 is a global test upon the body. V02 requires: (1) the lungs, (2) the perfusion of oxygen into the blood (pulmonary arteries), (3) the heart (both heart rate and stroke volume), the cardiovascular system, ( heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries), (4) The musculoskeletal system ( muscles, fascia, tendons, ligaments, skeletal joints), (5) cellular metabolism, specifically mitochondrial respiration (The most prominent roles of mitochondria are to produce the energy currency of the cell, ATP (i.e., phosphorylation of ADP), through respiration, and to regulate cellular metabolism.
Preparation for Testing
Preparation for Testing includes: one or more of the following: A graded exercise test with a gas analyzer on a treadmill or recumbent bike, 3D body scan, and a gas analyzer metabolic test. ( 2 hrs to complete all tests)
*** Arrive 15 mins prior to testing – Read and Sign all forms.
*** Ask questions or voice concerns before testing
Cardiorespiratory Exercise Test (V02 Max)
*** Fast 4 hrs prior to testing (No coffee or stimulants – water is ok)
*** Avoid OTC Cold medications ( Continue with Prescribed Meds)
*** Do not exercise 24 hrs before testing
*** Wear Exercise Cloths for V02 Testing ( Wear comfortable shoes)
Resting Metabolic Testing (RMR)
*** Fast 4 hrs prior to testing ( No coffee or stimulants – water is ok)
*** No exercise 24 hrs prior to testing
3D Body Composition Scan
*** Wear very tight fitting cloths for 3D Scan – It is measuring your body exactly
*** Tie up your hair for 3D Scan
*** Snug Shorts / Sport’s Bra / Tight Leggings / Etc.
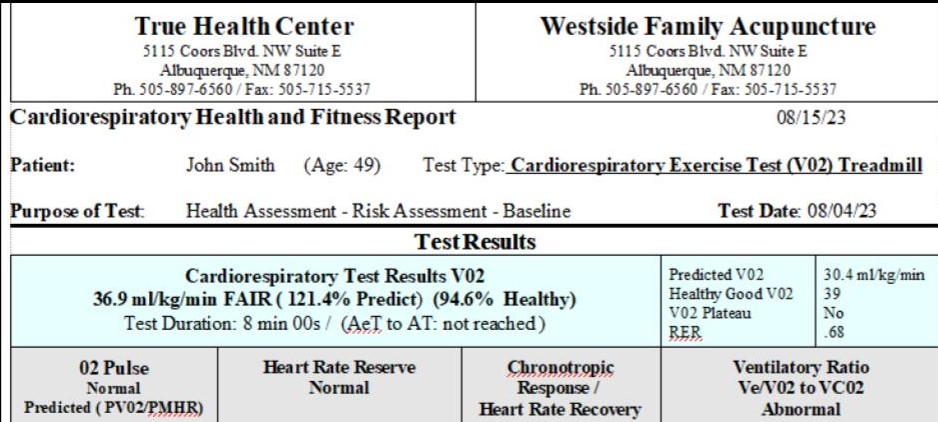
Medical V02 Interpretation
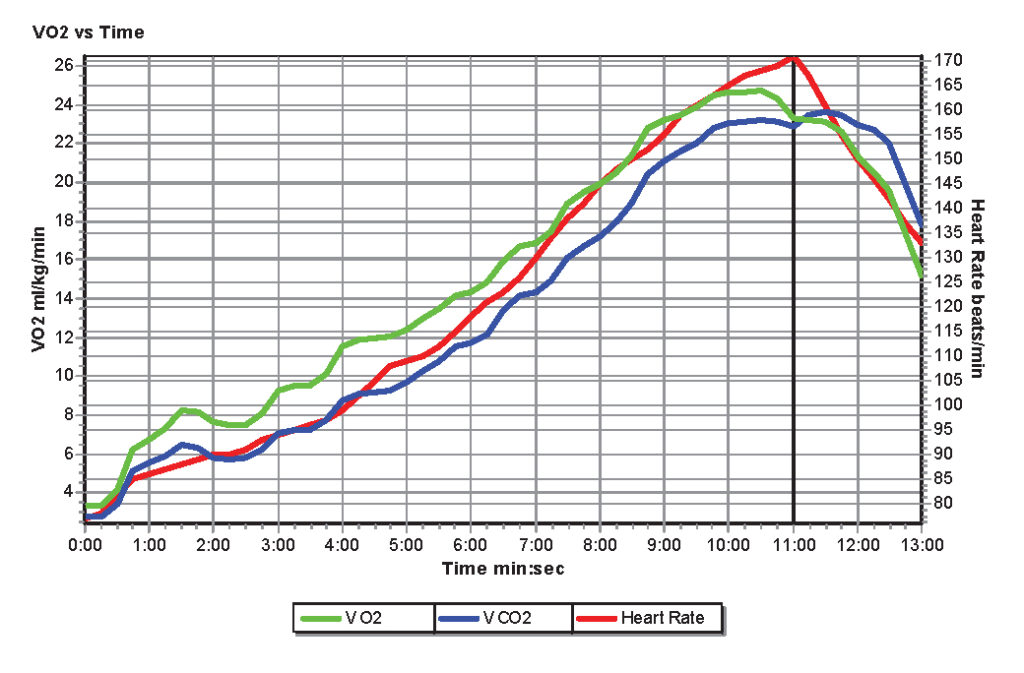
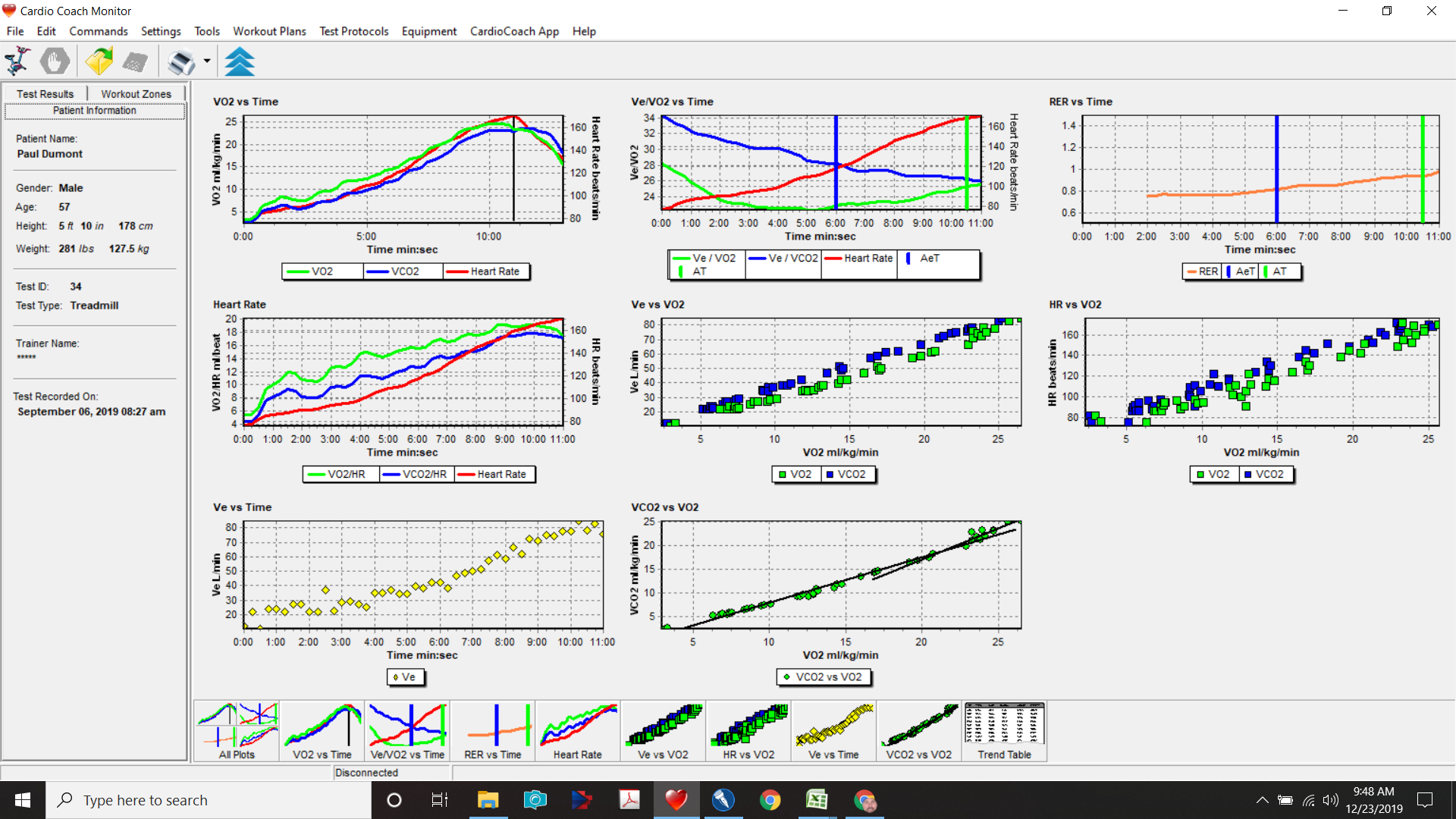
V02 Cardiorespiratory Test Measurements (V02 Max)
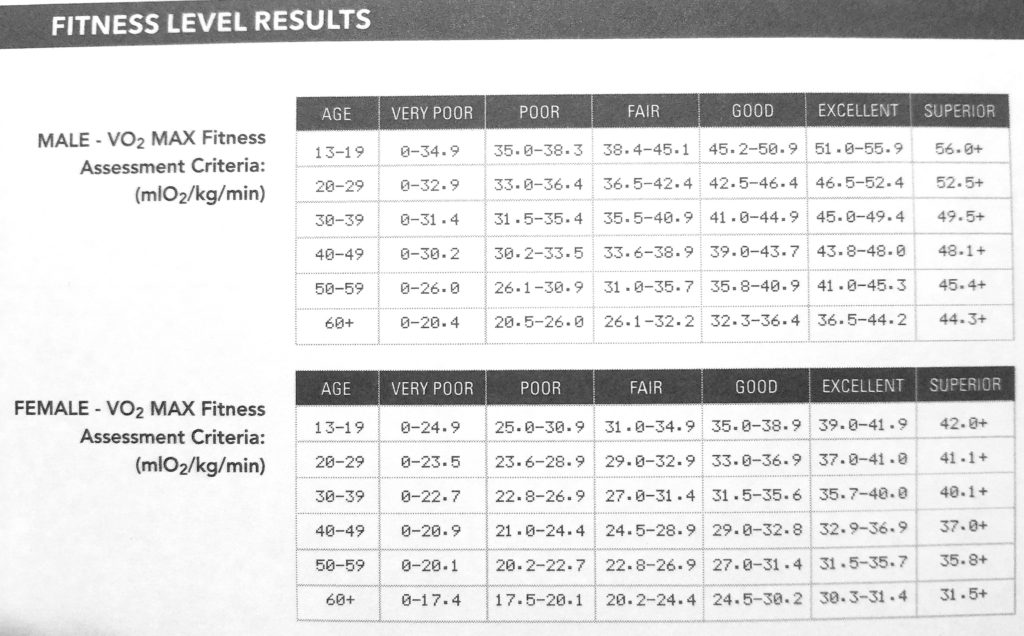
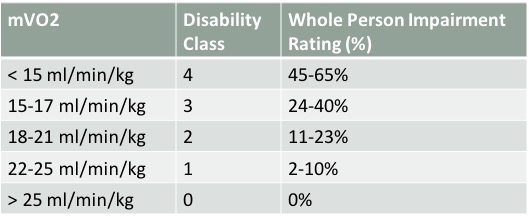
- V02 Score : The Maximum or Peak Amount of Oxygen Your Body can Extract in 1 minute. This is your V02 Max or Peak. This is a very very important number. In fact this number has become the most important vital signs of current status and predictor of future health.
- VE: Minute ventilation (VE) is the quantity of air moved into and out of the lungs in one minute (Tidal Volume multiplied by Respiration Rate) and dictates CO2 elimination from alveoli. Pretesting with spirometry gives a predicted maximum ventilation that one should need less then <80% during the test. If this is not achieved, possible pathologies are considered.
- VE/VO2, which identifies the relationship between ventilation and oxygen consumption. Ventilatory Equivalents for Oxygen (VE/VO2): refers to number of liters of ventilation per liter of oxygen consumed. The normal value is typically around 25-30 and increases once the person reaches their ventilatory threshold. High values are a marker of inefficient ventilation, which can be due to hyperventilation or increased dead-space, a marker of poor gas exchange. For unknown reasons, subjects with heart failure have a high VE/VO2. On the exercise data sheet this term will be denoted by “EqO2”
- VE/VC02 Ventilatory Efficiency Slope: The most studied parameter in this regard is the relationship between minute ventilation and carbon dioxide output (VE/VCO 2 ), also called ventilatory efficiency slope. The rise in VE and VCO 2 is strictly linked during aerobic exercise since increased VCO 2 levels due to the increased metabolism drive ventilation. In healthy individuals, the values of VE/VCO 2 slope are usually lower than 30.
- Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER): is the ratio between the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) produced in metabolism and oxygen (O2) used.
- Heart Rate: is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body’s physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide
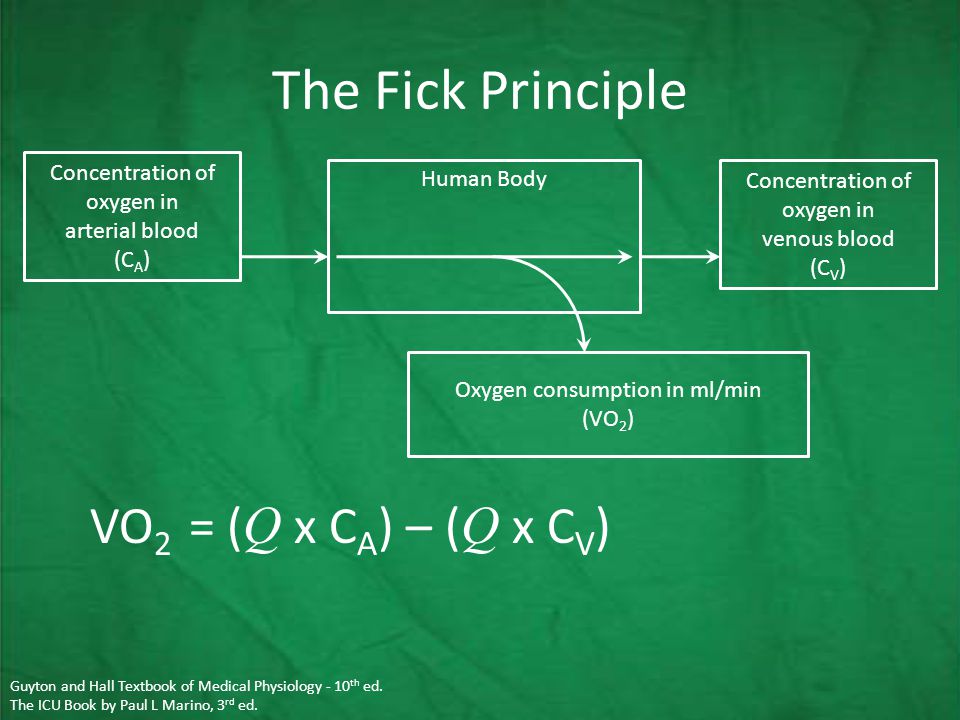
- Oxygen Pulse: refers to the volume of oxygen taken up by the pulmonary blood per heartbeat. It is calculated by dividing the VO2 by the simultaneously measured heart rate. The units are ml O2/beat. The term is derived from the Fick equation and equals the product of stroke volume and the arterial-mixed venous oxygen difference [C(a-v)O2], If one assumes that C(a-v)O2 reaches a steady state at maximal exercise, then the oxygen pulse can be used as a surrogate measure for stroke volume. The normal value depends on the size of the subject but can range between 8 and 18 ml O2/heart beat
- C02 Output: refers to the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled from the body per unit time. It is expressed in ml/min. A normal value at rest is around 200 ml/min. This value increases with progressive exercise. It continues to rise after the completion of exercise as the muscles continue to eliminate carbon dioxide before returning to baseline levels after several minutes. Note that carbon dioxide output can differ from carbon dioxide production by the body’s metabolic processes but in the steady state production and output are the same
- Aerobic Metabolism: is the way your body creates energy through the combustion of carbohydrates, amino acids, and fats in the presence of oxygen. Combustion means burning, which is why this is called burning sugars, fats, and proteins for energy. Aerobic metabolism is used for the sustained production of energy for exercise and other body functions. Examples of exercises that use aerobic metabolism include walking, running, or cycling with sustained effort.
- Anaerobic Metabolism: is the creation of energy through the combustion of carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. This occurs when your lungs and/or heart, and/or vascular system cannot put enough oxygen into the bloodstream to keep up with the demands of your muscles for energy. It generally is used only for short bursts of activity, such as when you sprint when running or cycling or when you are lifting heavy weights.
- Anaerobic Threshold: (AT) is the exertion level between aerobic and anaerobic training. The AT is the point during exercise when your body must switch from aerobic to primarily anaerobic metabolism. Further, (AT) is the physiological point during exercise at which lactic acid starts to accumulate in the muscles, which occurs around the point during increasing intensity exercise that anaerobic processes become more dominant. For this reason it is also sometimes called the Lactate Threshold (LT).
- SP02: stands for peripheral capillary oxygen saturation, an estimate of the amount of oxygen in the blood. … SpO2 is an estimate of arterial oxygen saturation, or SaO2, which refers to the amount of oxygenated haemoglobin in the blood. Haemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in the blood.
- Blood Pressure: The force of circulating blood on the walls of the arteries. Blood pressure is taken using two measurements: systolic (measured when the heart beats, when blood pressure is at its highest) and diastolic (measured between heart beats, when blood pressure is at its lowest). Blood pressure is written with the systolic blood pressure first, followed by the diastolic blood pressure (for example 120/80).
- Peak Circulatory Power: Cardiac power, the product of CO and mean arterial pressure, is a powerful index of cardiac systolic function (42). Circulatory power is a cardiac power surrogate obtainable from cardiopulmonary exercise testing, calculated as peak VO2 (in milliliters per kilogram per minute) multiplied by peak systolic blood pressure
- Ventilatory Power: Minute ventilation/CO(2) production (VE/Vco(2)) slope is an index determined by cardiopulmonary exercise testing, which incorporates pertinent cardiac, pulmonary, and skeletal muscle physiology into a substantive composite assessment. The VE/Vco(2) slope has many applications, including utility as a well-validated prognostic gauge for patients with heart failure (HF). We combine VE/Vco(2) slope with systolic blood pressure, creating a novel index that we labeled ventilatory power. Ventilatory power links the combined physiology inherent in the VE/Vco(2) slope to peripheral pressure, adding an additional dimension pertinent to HF assessment. Whereas the related concept of circulatory power links peak oxygen consumption with peak systolic blood pressure as a prognostic index, so ventilatory power would provide greater prognostic discrimination than VE/Vco2 slope, peak oxygen consumption, and circulatory power for patients with systolic HF.
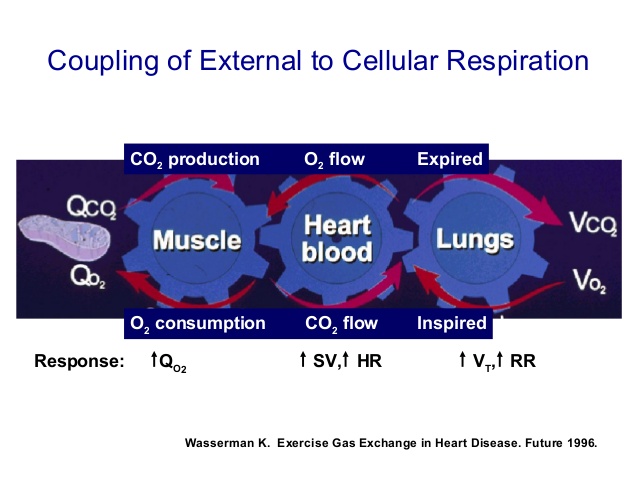
- Definitions of Oxygen delivery and utilization systems. VE = minute ventilation; BF = breathing frequency; TV = tidal volume; P AO2 = alveolar oxygen partial pressure; P ACO2 = alveolar partial pressure
of carbon dioxide; Q = cardiac output; SV = stroke volume; HR =
heart rate; DO2 = oxygen delivery; CaO2 = arterial oxygen content; SaO2 = arterial oxygen saturation; Hb = haemoglobin;
CvO2 = mixed venous oxygen content; SvO2 = mixed venous oxygen saturation; a-vO2 difference = arterio-venous oxygen difference; La + = lactate
Resources
The Human body is about two-thirds Oxygen!
You’ve got a lot of this one. Oxygen makes up a whopping 65 percent of the human body by weight. But that doesn’t mean you’re just full of air. Most of the oxygen in your body is bound to hydrogen in the form of water. You’ve heard it before, but it’s true that the human body is around 60 percent water, and that’s most of your oxygen. That water is more than weight — it helps the body to regulate temperature and osmotic pressure.